Introduction to Autonomous Farming Technologies
As the global population continues to rise, the agricultural industry faces increasing pressure to produce more food efficiently and sustainably. Autonomous farming technologies have emerged as pivotal solutions, significantly transforming traditional farming practices. These innovations encompass a range of tools and systems that leverage automation, robotics, and artificial intelligence to optimize agricultural productivity.
What Are Autonomous Farming Technologies?
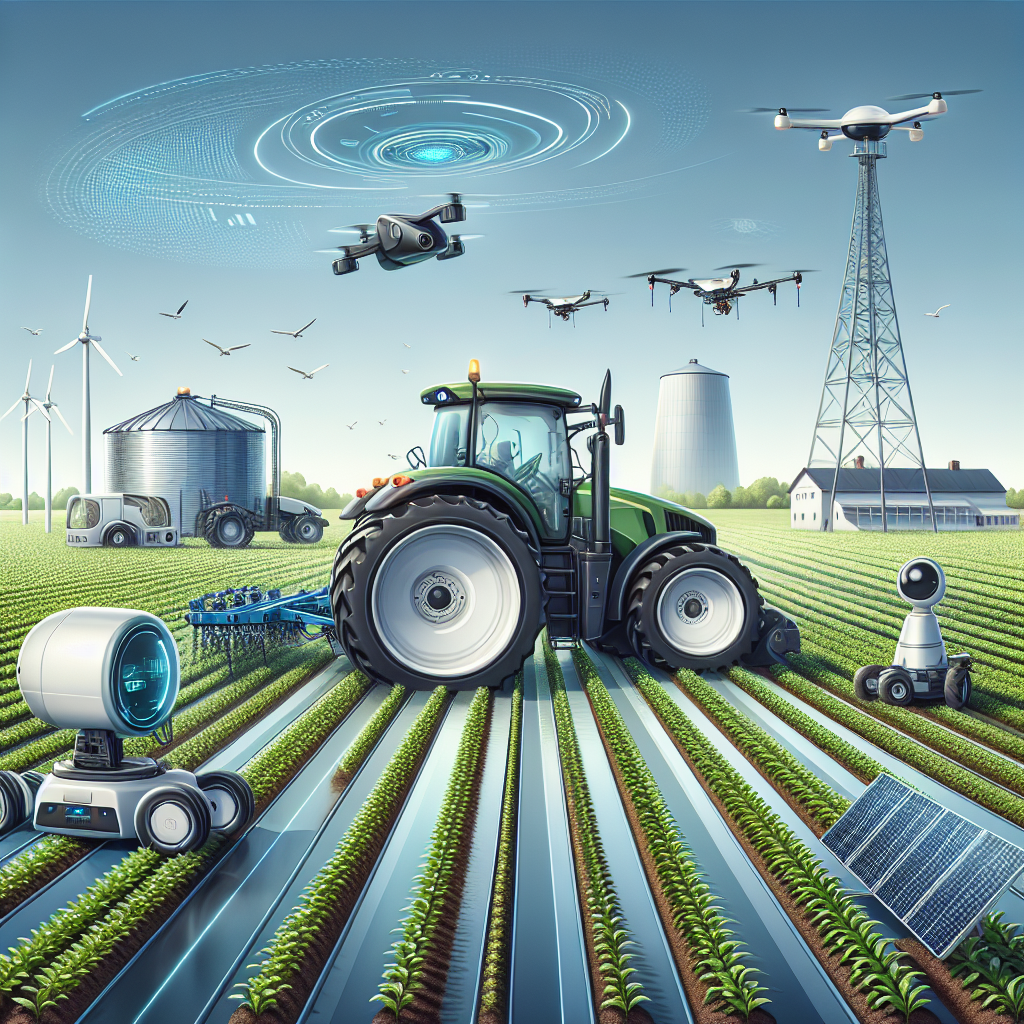
Autonomous farming technologies refer to the use of automated systems and machines that can operate independently in agricultural settings. These technologies aim to reduce the need for human intervention, improve efficiency, and minimize costs. Some key components of autonomous farming include:
- Autonomous Tractors: Equipped with GPS and AI, these tractors can navigate fields and carry out tasks such as plowing, planting, and harvesting.
- Robotic Harvesters: These machines identify ripe crops and harvest them with precision, reducing waste and labor costs.
- Drone Technology: Drones are utilized for crop monitoring, planting seeds, and applying fertilizers or pesticides, ensuring quality while minimizing resource use.
- Automated Irrigation Systems: Smart irrigation systems adjust water usage based on soil moisture levels, enhancing efficiency and sustainable water use.
Benefits of Autonomous Farming
The integration of autonomous farming technologies offers numerous benefits, including:
- Increased Efficiency: Automation allows farms to operate continuously with fewer labor costs, maximizing productivity.
- Sustainability: By optimizing resource use, these technologies promote sustainable practices, helping to preserve the environment.
- Higher Crop Yields: Precision farming techniques enable farmers to apply the right amount of nutrients and water, leading to higher yields.
- Data-Driven Decisions: The use of sensors and AI provides real-time data, allowing farmers to make informed decisions based on analytics.
Challenges and Considerations
While autonomous farming technologies offer significant advantages, there are challenges to consider:
- Initial Investment: The cost of implementing advanced technologies can be high, creating barriers for smaller farms.
- Technical Knowledge: Farmers may need training to operate and maintain sophisticated equipment effectively.
- Security Risks: As with any technology, there is a potential risk of cyberattacks on autonomous systems.
The Future of Autonomous Farming
The future of autonomous farming is promising, with continuous advancements paving the way for smarter agricultural practices. As technology evolves, we can expect:
- Integration of AI: More AI-driven decision-making tools that enhance efficiency and reduce human error.
- Collaborative Robots: Enhancements in robotic technology that work alongside human labor for more complex tasks.
- Global Reach: Wider adoption in developing countries, improving food security and sustainability on a global scale.
Conclusion
Autonomous farming technologies are poised to revolutionize agriculture by making it more efficient, sustainable, and productive. As these technologies continue to develop, farmers who embrace innovation will be better equipped to meet the challenges of modern agriculture. Adopting autonomous practices not only benefits individual farmers but also plays a crucial role in feeding the growing world population sustainably.



Leave a Comment